Introduction
Ocean waves driven by wind stress—wind-waves—are familiar and often impressive, bringing the benefits of renewable energy and recreational activities like surfing, but frequently acting as hazards to coastal and offshore industries. For example, in recent years extreme levels of erosion on coasts of the European Atlantic (Masselink et al., 2016) and US Pacific (Barnard et al., 2017), attributable to extremely energetic wave conditions, have been reported. Barnard et al. (2017) showed that wave energy incident to the US Pacific coast, linked to the strong El Niño of 2015/2016, contributed to the largest observed integrated wave energy based on historical records. However, possible changes in wave intensity are not always the most important finding because waves are complex and multivariate phenomena. Harley et al. (2017) attributed the most severe coastal erosion observed in southeast Australia in 40 years to the joint effect of wave height and (anomalous) wave direction. With changing polar climate, there has been substantial interest in wave-sea ice interaction (Doble and Bidlot, 2013; Casas-Prat et al., 2018), with wave action linked directly to Antarctic ice-shelf collapse (Massom et al., 2018). Island nations in particular are susceptible to changes in wave conditions (Hoeke et al., 2015; Duvat et al., 2016), and such severe impacts, noted in particular by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC; IPCC, 2014), motivate efforts such as the Coordinated Wave Climate Intercomparison Project (COWCLIP; Hemer et al., 2012, 2013a; X.L. Wang et al., 2016) that is in part supported through the submission of simulated global and regional wave climate data sets, two of which are described in this paper.
With a strong research imperative, studies have focused on both historical and future conditions in various ways. Satellite and data buoy observations capture both the climate (Ruggiero et al., 2010; Izaguirre et al., 2011; Young et al., 2012) and specific events (D.W. Wang et al., 2005), while reanalysis data have been analyzed using dynamical and statistical methods (Camus et al., 2014). Dynamical projections typically involve the generation of near-surface winds using a (possibly coupled) atmosphere model that can then be used to derive ocean waves either statistically (X.L. Wang and Swail, 2006; Perez et al., 2015; Camus et al., 2017) or dynamically (Hemer et al., 2013b) using a global wave model such as WAVEWATCH III (WW3; Tolman, 2014). So-called “phase-averaged” global models such as WW3 employ an averaged spectral representation of waves and do not resolve individual waves (Komen et al., 1994), including extreme “rogue waves,” although they can be informative (Babanin and Rogers, 2014). WW3 has been used widely for global (Timmermans et al., 2017) and regional studies (Shimura et al., 2016; Aguirre et al., 2017), and wave energy resource assessment (Mackay et al., 2010; Hemer et al., 2017).
Research suggests that wave climate may change substantially in the future, with considerable regional variation (Hemer et al., 2013a; Erikson et al., 2015; Shimura et al., 2016; Aarnes et al. 2017; Casas-Prat et al., 2018). Erikson et al. (2015) evaluate wave climate in the eastern north Pacific and report changes in both mean and extreme wave conditions, driven predominantly by extratropical cyclones (ETC) in the mid-latitudes, with a generally decreasing trend with severity of greenhouse gas forcing. Swell generated by ETCs in the Southern Ocean—consistently the roughest on Earth (Young 1999)—is likely to result in future increases in wave height (Hemer et al., 2013a) that may contribute to inundation threat to islands in the western tropical Pacific (Shope et al., 2016). Shimura et al. (2016) found that winter wave conditions in the western North Pacific were dominated by ETCs with intensity set to decrease under future scenarios. They remark in particular that local coastal conditions, and resultant impacts, in Japan are a complex function of wind-sea and remote swell and advocate for focused high-resolution regional studies in such areas in order to attribute effects.
Extreme wave conditions that typically present the greatest risks are also set to change (Fan et al., 2013; X.L. Wang et al., 2014; Barnard et al., 2017; Shimura et al., 2015, 2016, 2017), although investigation of extremes can be substantially more challenging than assessment of means. Inference about extremes (Coles, 2001; see also section on Extreme Value Analysis) requires long time series of output to robustly quantify the probability of rare events. Furthermore, a model may be limited in its ability to accurately reproduce physical processes responsible for extremes. Many of the aforementioned studies are concerned with impacts from waves driven by ETCs—large synoptic-scale storms—that typically originate in the mid-latitudes and impact the coasts of northern Europe and the northwestern United States. Being spatially broad, sometimes covering thousands of kilometers, they allow waves to develop over very long fetch. Numerical investigation can be very effective for storms of this kind, which are typically well resolved at horizontal resolutions around 1° (~100 km). Such simulations are affordable to run and output is abundant (Taylor et al., 2012). In contrast, tropical cyclones (TC) are not well resolved at spatial and temporal resolutions typically employed in global atmosphere simulations (Timmermans et al., 2017), but they are clearly important to atmospheric and oceanic climate and impacts (Sriver, 2016; S.S. Chen and Curcic, 2016).
“Both the devastating 2017 North Atlantic hurricane season and growing evidence for the connection between tropical cyclone activity and increasing ocean temperature motivate investigation of possible future changes.”
While damage from hurricanes (the strongest TCs) is the dominant economic cost from “billion dollar” natural disasters (~63% of total) in the United States (NOAA NCEI, 2018), 2017 in particular was a stark reminder of the threat of hurricanes to society. Three major hurricanes made US landfall, setting records, including the most rainfall in a single storm (Harvey) and the largest annual losses due to hurricanes in US history (Munich RE, 2018). Hurricane costs attributable to waves are difficult to ascertain because wind, waves, and storm surge act in combination, but they can be substantial. During Katrina, 1,500 people lost their lives on shore due to storm-surge-related flooding, while offshore, dozens of oil and gas platforms were damaged or destroyed, resulting in near total shutdown of the Gulf of Mexico’s offshore production.
Research on TC climatology and related effects at the atmosphere-ocean boundary, including waves, is challenging. TCs and hurricanes form from atmospheric disturbances typically at least 5° north or south of the equator. When developed, the structure of the storm’s center—the eye—is typically smaller than ~100 km and thus, where numerical simulation is required, resolution needs to be significantly higher than this in order to even approximate the process. High-resolution coupled modeling, required to resolve various complex effects (Zambon et al., 2014; S.S. Chen and Curcic, 2016; Fan and Rogers, 2016), remains prohibitively expensive for climatological study. Nonetheless, it turns out that atmospheric simulations below ~60 km horizontal resolution can produce realistic TC climatology (Murakami et al., 2012, 2015). Furthermore, use of fixed sea surface temperature (SST) boundary conditions (Hurrell et al., 2008), in place of a dynamic ocean, reduces computational cost, rendering this kind of approximate approach feasible for well-resourced institutions. Resulting winds, including TCs, can be used to drive a wave model, although such studies remain sparse (Fan et al., 2013; Shimura et al., 2015; Timmermans et al., 2017).
In this paper, using such a numerical approach, we augment the investigation of Timmermans et al. (2017) by presenting two future wave climate data sets and an analysis of changes in the extremes, in terms of the 20-year significant wave height, Hs, return level. The two scenarios follow the Half a degree Additional warming, Prognosis and Projected Impacts (HAPPI) protocol (Mitchell et al., 2017), representing 1.5°C and 2.0°C stabilized climates agreed upon as long-term targets to mitigate severe climate change impacts by members of the United Nations as part of the 2016 Paris agreement. However, cognizant of possible uncertainties introduced through this approach, and discussed further in the next section, we also make use of recent hindcasts of a number of major US hurricanes. This allows us to compare directly with observations from data buoys and investigate sources and magnitudes of error that may exist in approximate climatological simulations. We find a tendency toward excessively extreme Hs, but with accuracy in more benign conditions, which raises questions about the validity of simulations of (extreme) wave climate and motivates further research and corrective strategies. In the following section, we elaborate further on our understanding of TC and wave climate, and investigate it through numerical approaches. Our approach to wave modeling, and subsequent application of extreme value analysis are described next. We then discuss results of the analysis of future extreme wave climate and describe the hurricane wave simulations and their analysis. We briefly offer our conclusions in the final section.
Tropical Cyclones and Waves
Energetically, TCs can be considered to be a Carnot heat engine, powered by energy from warm ocean surface waters. The dependence of TC genesis and evolution on SST has been studied at length (Emanuel, 2005; Vecchi and Soden, 2007a), although properties of the atmosphere such as the temperature of the tropopause (Emanuel et al., 2013) and vertical wind shear (Vecchi and Soden, 2007b) are particularly influential. Feedback from the ocean is also important: mixing of cooler subsurface water by induced turbulence reduces heat availability and results in less-favorable conditions. Seroka et al. (2016) show that during Hurricane Irene (2011), “ahead-of-eye” cooling of coastal surface waters due to currents induced by Irene itself, was a key causal factor in rapid de-intensification before making landfall. Conversely, the availability of warmer subsurface water may support particularly powerful events, as speculated for “Super Typhoon” Haiyan in 2013 (Lin et al., 2014). A steepening subsurface temperature gradient under global warming may give rise to a greater cooling effect, thus suppressing intensification in future climates (Huang et al., 2015). TC activity is also linked to the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (Patricola et al., 2014, 2016; Zhang et al. 2016), but as Murakami et al. (2017) point out, many factors are influential, and a strong El Niño does not solely predicate an active hurricane season. In general, the question of how climate change is affecting TC climatology remains the subject of debate (Sobel et al., 2016).
Ocean waves arise from momentum transfer through wind stress—a function of surface drag—itself affected by the waves (Komen et al., 1994; Moon et al., 2003). However, complex atmosphere-ocean-wave interactions, particularly under extreme conditions, remain poorly understood. Y. Chen and Yu (2017) found that choice of wind stress parameterization resulted in differences of up to 12 m in peak wave heights under hurricane conditions. Research has also examined turbulent mixing by waves (Aijaz et al., 2017) and the effect of induced currents on wave height around the eye of the hurricane (Fan et al., 2009). Investigation of these complex interactions typically requires high (~ few kilometers) resolution coupled simulations (Zambon et al., 2014; S.S. Chen and Curcic, 2016), but in general, the use of coupling in climatological simulations remains limited. For example, coupling between atmosphere-wave (Fan et al., 2013) and atmosphere-ocean (Li and Sriver, 2018) is possible on short (~100 year) climatological timescales. However, Fan et al. (2013) report that the high-resolution atmospheric model (HiRAM; ~ 50 km resolution) generates few major hurricanes. In addition, although the Community Earth System Model (CESM; ~25 km resolution) has been shown to produce remarkably good TC intensity distributions, including major hurricanes, when using fixed SSTs (Wehner et al., 2015), Li and Sriver (2018) show that coupling the atmosphere to both slab and dynamic ocean alleviates spatial bias in TC storm track distribution seen in the uncoupled case. In general, however, tropical SST biases common to generations of coupled climate models (Zuidema et al., 2016) are known to cause substantial errors in simulated TC activity, with an under-simulation of 50% in the Atlantic and over-simulation of 80% in the east Pacific (Wei-Ching Hsu, Texas A&M University, pers. comm., 2018). Noting the unavoidable uncertainties, and difficulty in finding a tractable approach, the computational advantage of using fixed SSTs is attractive, and this configuration has been used widely. Mizuta et al. (2017), for example, ran 5,000 years of global atmospheric simulations at 60 km horizontal resolution, sufficient to resolve the TC frequency distribution, although statistical bias correction methods are required to investigate the most intense TCs, because they cannot be resolved numerically. Shimura et al. (2015) used some of those simulations to examine extreme wave heights from TCs in the western North Pacific, alleviating the conditionality on fixed SSTs by using an ensemble. The analysis of extreme wave climate in this study (see section on Changes in Extreme Wave Climate) therefore utilizes atmospheric simulations bounded by fixed SSTs, acknowledging uncertainties associated with the approach described above.
Approach to Wave Modeling
The approach to wave climate modeling and analysis follows Timmermans et al. (2017), briefly summarized here. In the later section on Hurricane Wave Modeling, we also make use of 10 m winds from high-resolution (3 km, 4.5 km, and 27 km) simulations drawn from ensembles of individual hurricanes employing fixed (observed) SSTs generated by the Weather Research and Forecasting Model (WRF; Skamarock et al., 2008). For these, the wave model configuration is similar to that described here but employs regional grids (Gulf of Mexico and tropical western Atlantic) at similar resolutions (4 km and 27 km) and appropriate integration time steps. Note that in those cases, focusing on the locally generated hurricane waves, sea surface boundaries were left open, thus ignoring remotely generated wave systems. More discussion of the WRF simulations is provided in the section on Hurricane Wave Modeling.
For global climate, 10 m three-hourly winds at ~25 km horizontal resolution were obtained from simulations of the atmosphere using the CESM (Hurrell et al., 2013) bounded by SST patterns commensurate with +1.5°C and +2.0°C stabilized climates. Specifications of SST patterns are given by Mitchell et al. (2017; their section 2.1) but, to summarize construction of the +1.5°C scenario, the difference between the average of 2090–2100, taken from Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 5 (CMIP5) RCP2.6 scenario ensemble, and the average of 2006–2015, is added to observed SSTs for 2006–2015. Five independent CESM simulations, each initialized with a microscopically perturbed atmospheric state, generate winds for the 10-year period “2106–2115,” which are then used to force WW3. For each scenario, we make the assumption that each year of output is an independent sample in a stationary climate, thus providing 50 years for extremal analysis. WW3 is configured on a 0.25° global grid (corresponding approximately to the resolution of the forcing winds), utilizing ST4 input and dissipation scheme and NL1 (DIA) nonlinear interactions (see Timmermans et al., 2017, for more details), with three-hourly output of global fields of various wave parameters. Hs at each model grid cell is analyzed using an extreme value approach, outlined in the next section. Note also that in the section Changes in Extreme Wave Climate, we compare output in terms of 20-year return level to output from a similar 44-year data set representative of present-day climate, described in Timmermans et al. (2017).
Extreme Value Analysis
Extreme value (EV) theory is an active area of statistical research (Coles, 2001; Davison and Huser, 2015) and of ever-increasing importance in environmental studies, as interest in future extreme events grows (Risser and Wehner, 2017). It provides a statistical framework for the study of rare events and allows us to estimate, for example, return levels and periods of wave height. The use of univariate EV theory is now fairly common and facilitated by many off-the-shelf packages, such as the extRemes (http://www.assessment.ucar.edu/toolkit/) package for R (https://www.r-project.org/). Méndez et al. (2006), for example, make use of EV theory to investigate trends in extreme Hs in the northeastern Pacific. However, many questions exist about more complex multivariate extreme phenomena where methodological challenges remain substantial (Davison and Huser, 2015). Here, following Timmermans et al. (2017), we make use of the “peaks-over-threshold” (POT) method (Coles, 2001), which involves statistically modeling threshold exceedances of Hs (typically >97.5 percentile), in order to derive an EV distribution (EVD) from which 20-year return levels can be derived. Note that estimates of decay rate in the tail of the probability distribution can be sensitive to the occurrence of a single high-magnitude event so here, noting the high spatial variability of extreme waves, we actually employ a dynamic threshold algorithm to fit the EV model more robustly.
For brevity, we omit further details of fitting an EVD and refer the reader to Timmermans et al. (2017), but we illustrate some important issues by examining observed and simulated wave height data. Figure 1 panels a and b show histograms for Hs at two NOAA data buoys that lay in the paths of hurricanes Irma and Maria, respectively. The general shape of the distributions is typical of the open ocean and is skewed, with a right-hand tail due to higher winds. Note that buoy 41047 (Figure 1b), showing a slower tail decay rate, lies in the North Atlantic and is exposed to more energetic conditions, in contrast to buoy 42060 (Figure 1a) that is more sheltered in the Caribbean (buoy locations are shown in Figure 3, bottom left panel). However, the distribution statistics tell us very little about the most intense events, which are so infrequent that they cannot be resolved in the figures—maximum, pre- and post-hurricane passages (blue and red arrows, respectively) are indicated.
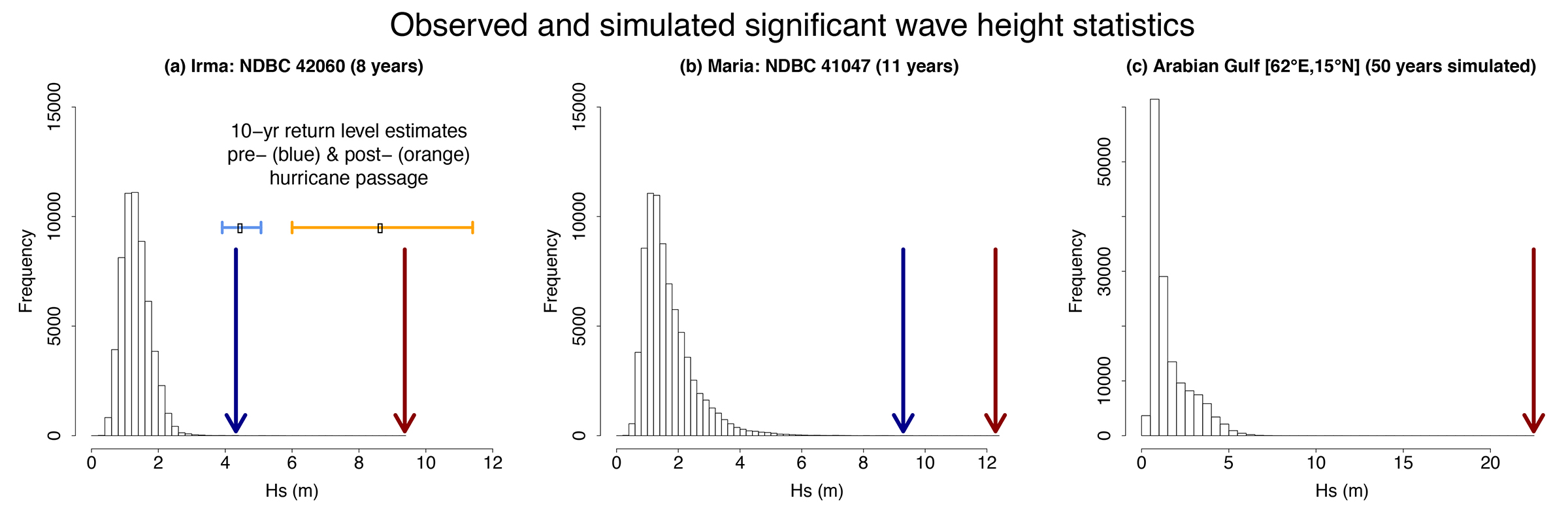
Figure 1. Histograms for significant wave height (Hs) at NOAA data buoys (a) 42060 (Central Caribbean Sea) and (b) 41047 (Hatteras Plain, Western Atlantic). Arrows indicate the maximum value before (blue) and after (red) hurricane passage. Panel (c) shows 50 years of simulation output, with the (red) arrow indicating the maximum value. > High res figure
|
An EVD could be fitted using a POT approach to model the occurrence of the extremes; however, in these cases we can see that in approximately 10 years of observations, the variability in the maximum is substantial—a single event can result in an increase in the maximum of between 25% and 100%. In fact, at buoy 42060, the single event of hurricane Irma is responsible for all observations in the highest 50% of the range of the data, so we have only a single independent data point (high threshold exceedance) from which to infer extremal behavior. Figure 1a includes point estimates and 95% confidence intervals, based on the statistical sampling only, for 10-year return levels for Hs. The estimates were derived from the data excluding (light blue) and including (orange) the passage of Irma, revealing that the earlier 95% confidence interval does not bound wave heights from the passage of Irma, and in fact suggests them to be extremely unlikely. In this case, the short duration of the observational record with respect to the frequency of TC passage (and extreme waves) in this region limits our ability to infer extremal behavior. For comparison, Figure 1c shows an example of a histogram of Hs from simulated wave climate (our +2.0°C data set of 50 years) at a location in the Arabian Gulf affected by TCs on an infrequent basis. Note that the maximum value of approximately 22.5 m is indeed extreme, exceeding the largest in the observed record of approximately 19 m, which was in the North Atlantic and not due to a TC.
Changes in Extreme Wave Climate
We fitted independent EVDs to each grid cell for each of the 50-year wave climate data sets and obtained 20-year return levels for Hs. We compare these to a similar (44-year) data set described by Timmermans et al. (2017) in order to evaluate changes. Figure 2 shows differences in 20-year return levels for Hs between future +1.5°C and the present day (panel a), +2.0°C and the present day (panel b), and +2.0°C and +1.5°C (panel c). In terms of magnitude of change, Figure 2 panels a and b look remarkably similar to each other, and also to Figure 3c of Timmermans et al. (2017), which shows the difference between the present day and the future RCP8.5 scenario. These results indicate only small differences in extreme wave climate between the future scenarios. However, there may be evidence of some large regional changes, of many meters, between present-day and future scenarios. A higher density of storm tracks in the central and eastern Pacific is seen in all future scenarios, with possible evidence of a reduction in extreme waves (due to reduced TC activity) in the Pacific east of Australia.

Figure 2. Differences in Hs 20-year return level between (a) +1.5°C and the present day, (b) +2.0°C and the present day; (c) +2.0°C and +1.5°C. Stippling indicates areas where the difference is estimated to be statistically significant. > High res figure
|
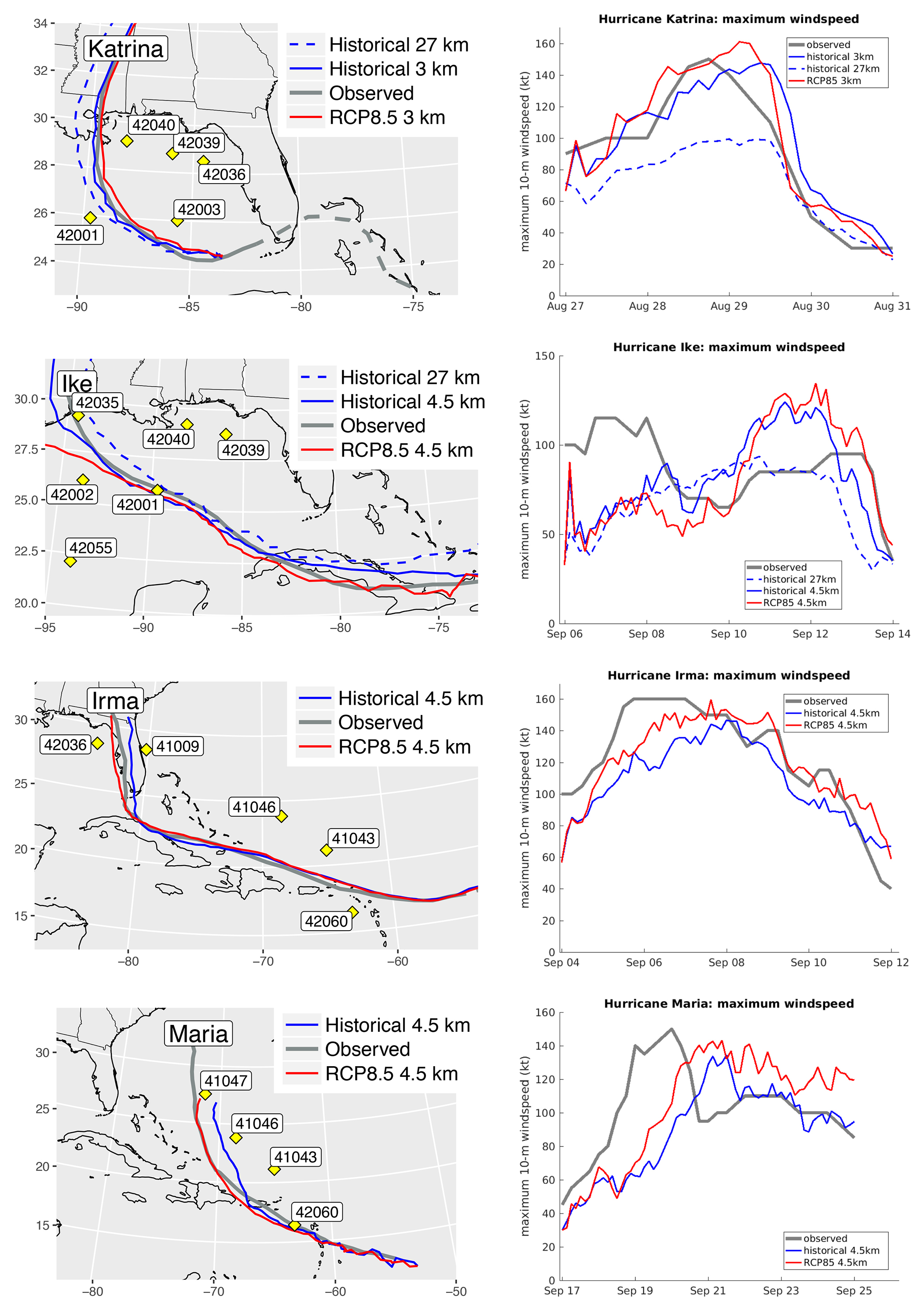
Figure 3. (left panels) Hurricane tracks for the different simulations (for each scenario) used and locations of relevant NOAA data buoys. (right panels) Corresponding maximum wind speeds. > High res figure
|
These possible regional changes in extreme wave climate reflect the simulated distribution of storm tracks in the warmer scenarios, which raises questions about the shift. Li and Sriver (2018, their Figure 5a–h) show the difference between TC climatologies arising from fixed SSTs and a coupled ocean when simulated in CESM. With respect to observations and coupled modeling, fixed SSTs lead to a high bias in the density of TCs, particularly in the eastern Pacific and the Atlantic and Indian Oceans. Here, however, the easterly bias in TC track density associated with fixed SST simulations appears to be further compounded in the projected climate. In the South Pacific, east of Australia, where track density bias appears to be lower, a possible reduction in extreme wave heights is apparent. However, owing to the limited duration of the data sets, the extremes are substantially affected by individual TC tracks, and robust determination of differences is challenging. This is particularly problematic in areas of low frequency of passage of intense TCs. A particular example can be seen in Figure 2b in the Arabian Gulf, where a single event—bearing resemblance to Cyclone Gonu (2007)—dramatically affects the 20-year Hs return level (see also Figure 1c). Note that dark stippling provides an estimate of statistical significance of changes (calculated from estimates of the sampling distribution when fitting the EVD), revealing that robustness of difference is mostly limited to extremes arising from individual storms, including ETCs in the mid-latitudes. This challenge motivates both the generation of longer duration data sets and further detailed analysis of existing data (e.g., Shimura et al., 2017).
Hurricane Wave Modeling
The large Hs apparent in our data sets (max. 22.5 m), and reported in Timmermans et al. (2017), may be commensurate with excessive TC intensity in simulations using fixed SSTs, as suggested by Li and Sriver (2018). We elucidate this for waves from hindcasts of individual hurricanes, generated using WRF, with a fixed SST surface boundary condition. Although WRF and CESM differ in formulation and application, given the common lack of coupling, we anticipate errors in WRF-driven simulations to be informative with respect to potential errors in CESM. We have access to ensemble simulations of a range of hurricanes, designed to robustly detect response to increased SSTs (Patricola and Wehner, in press). These simulations employ local fixed-resolution grids of 3 km (for Katrina) and 4.5 km, and are forced by observed SSTs and lateral boundary conditions from NCAR’s Climate Forecast System Reanalysis (CFSR) data. Each ensemble is composed of 10 simulations for each of historic and RCP8.5 (observed +2.0°C elevated SSTs) scenarios. We studied four hurricanes—Katrina (2005, category 5), Ike (2009, category 4), Irma (2017, category 5), and Maria (2017, category 5)—and selected from each ensemble wind fields from the simulation that exhibited a storm track that corresponded most closely to observations. In the case of hurricanes Ike and Katrina, we also (fortuitously) have access to a single simulation at 27 km, commensurate with the resolution used for our climatological simulations. The output time step was set at 15 minutes. Wave fields were generated every 15 minutes using WW3, configured as described earlier in Approach to Wave Modeling. For these simulations in particular, unbounded numerical grids at 4 km resolution were employed, spanning the Gulf of Mexico (Katrina and Ike) and a region extended to the east to capture the coastal Atlantic (Irma and Maria). While this potentially excludes incoming wave systems crossing the grid boundary, no significant events were identified during the periods of interest, and observations suggest that the hurricanes were solely responsible for the extremes in each case. Furthermore, initial condition error was judged to be minimal, given that initial Hs observations were relatively small (<1 m) in all cases (see, e.g., Figures 5 and 6), and discrepancy with simulation output was also typically small, indicating that spin-up occurred within a few hours.
Figure 3 shows storm tracks and maximum wind speeds. While Hurricane Katrina principally impacted the Gulf of Mexico, the other three events had longer storm tracks spanning the outlying Caribbean islands. Figure 3 shows that the selected tracks, while similar, exhibit discrepancies from observation in space and time. Furthermore, the right-hand panels show discrepancies in the magnitude and timing of the maximum wind speeds, compared with HURDAT2 observations (http://www.aoml.noaa.gov/hrd/hurdat/Data_Storm.html). Spatial discrepancies tend to be small compared with the radius of the hurricane, although the divergence is more significant for Hurricane Maria. These discrepancies affect subsequent simulations of waves, although the objective is not to perfectly recreate each hurricane but rather, by comparison with observations, to elucidate sources of error and uncertainty in simulated extreme wave conditions.
We begin by comparing simulated 10 m wind speed (U10) and Hs with observations at a number of NOAA data buoys, and in the interest of brevity we only show more detailed results from Hurricane Ike. Note that other hurricanes were qualitatively similar in terms of deviation from observations. Simulations were conducted at 4 km and 27 km using historical winds, and at 4 km using winds conditioned on an RCP8.5 scenario forced by warmer SSTs. During Ike, the eye passed very close to buoys 42001 and 42019, thus providing an opportunity to examine the most intense part of the storm. Figure 4 shows comparisons of U10.
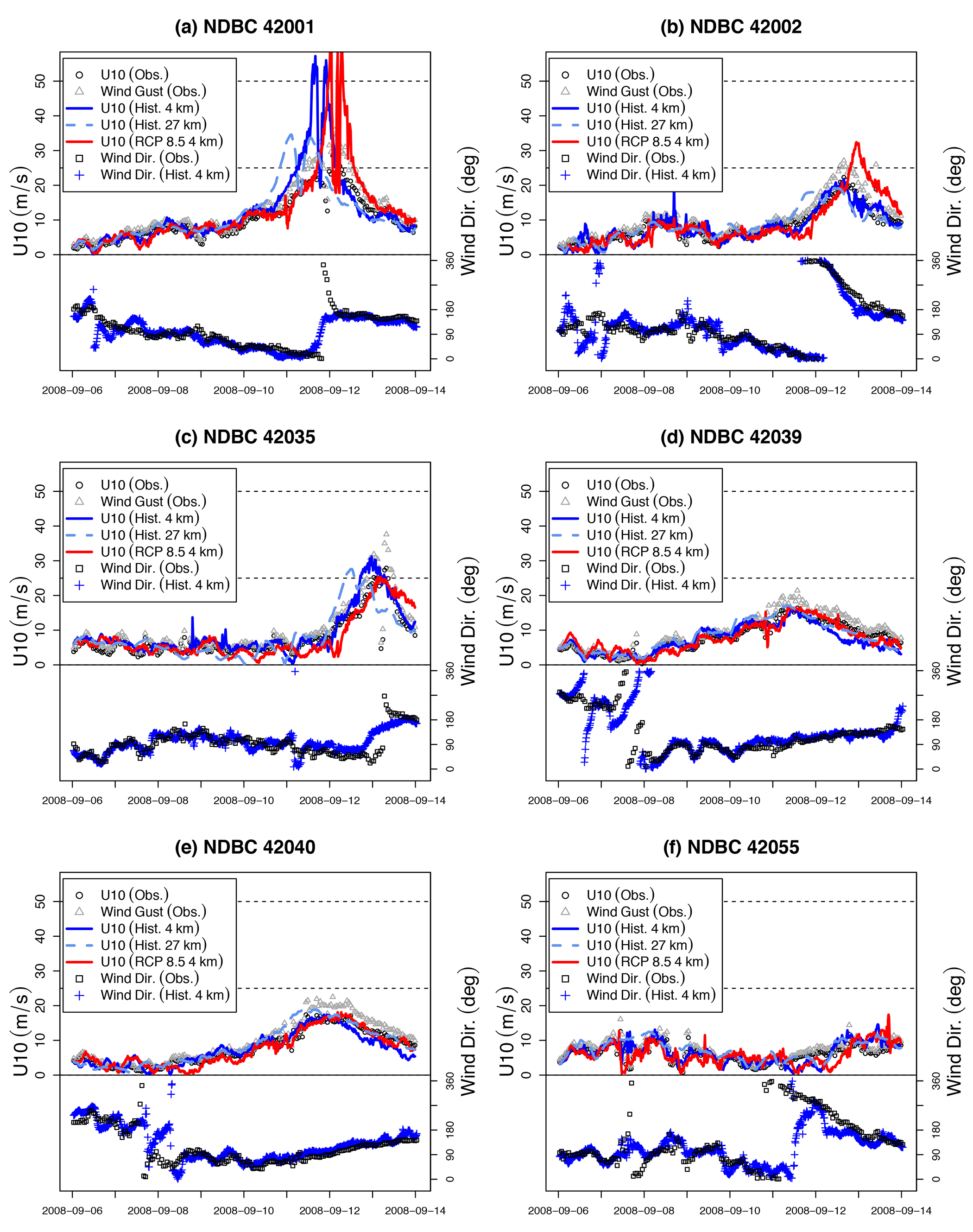
Figure 4. Hurricane Ike: Simulated 10 m wind speed (U10; top half of each panel, solid and dashed lines) under historical conditions at 4 km (blue), 27 km (light blue), and RCP8.5 winds, 4 km only (red) compared with observations from NOAA data buoys (circles and triangles), and wind direction (bottom half of each panel) simulated under historical conditions at 4 km (crosses) compared with observations (squares). > High res figure
|
The three simulations (historical, RCP8.5, and 27 km) reveal a range of agreement with observations, with several notable features. Considering the historical simulation (solid blue line) first, between Cuba and landfall in Texas, the simulated track coincided closely with the observed track. Agreement appears good with observations for both U10 and direction, with the exception of excessive U10 (>20 m s–1) at buoy 42001 in panel a. Buoy 42001 was fortuitously positioned in the path of Ike, and in fact, from both observations and simulation, the passage of the eye is indicated by a rapid drop in wind speed, around 2008-09-12 00:00, before a subsequent rapid increase. The high wind speeds shown in Figure 4a are commensurate with the discrepancy between simulated and observed peak wind speed estimates from HURDAT2 data shown in Figure 3. In contrast, at distances further from the hurricane’s eye, U10 agreement is much better. The RCP8.5 (red line) and 27 km historical (dashed blue line) cases show more variability, with discrepancies in timing and intensity. In particular, peak intensity of the 27 km run leads the others by at least 12 hours, likely due to errors in translation speed, seen also between the historical and RCP8.5 simulations. High wind speeds and temporal lag at buoy 42002 appear to be due to divergence of the track (red line), which passes much closer to 42002 than the historic track (see Figure 3), and makes landfall some 200 km west of observations. We also note there is no clear (visual) evidence that the RCP8.5 simulation consistently yields higher wind speeds, although the 27 km simulation does appear to generate 40% lower wind speeds at buoys 42001 and 42002. Note also that buoy 42035 is located in shallow water (15 m), where depth-induced breaking would be expected to constrain wave height in particularly energetic conditions.
We find that the characteristics of the wind speed are reflected closely in the wave simulations, shown in Figure 5. We compare simulation output to buoy measurements for Hs (top half panel) and peak period, Tp, (4 km historical simulation only, bottom half panel). Tp appears to be consistently well reproduced, generally falling within observational scatter (buoy observations typically lack uncertainty estimates). In general, discrepancies in Hs follow discrepancies in U10, with some variation. For example, historic U10 at buoy 42002 (solid blue line, Figure 4b) closely follows observations, but Hs exceeds observations by at least 2 m (solid blue line, Figure 5b). Discrepancies in U10 for the RCP8.5 and 27 km simulations also tend to be reflected in the Hs output. In general, large positive errors tend to occur close to the storm track, and much smaller, mostly negative, errors further away.

Figure 5. Hurricane Ike: Simulated Hs (top half of panel, solid and dashed lines) under historical conditions at 4 km (blue), 27 km (light blue), and RCP8.5 winds, 4 km only, (red) compared with observations from NOAA data buoys (circles), and peak wave period (bottom half of panel) under historical conditions at 4 km (blue dashed line) compared with observations (crosses). > High res figure
|
For comparison, Figure 6 shows similar analysis of Hs and Tp at the buoy location(s) showing the most intense conditions across all four hurricanes. Note in particular that buoy 42003 (Figure 6b) failed during Katrina (the first loss of a NOAA deep water buoy in 30 years of operations in the Gulf), hence the loss of data, and that the second peak in Hs, seen in Figure 6e, is in fact hurricane Jose (but not relevant here). Four of the six examples show maximum Hs that substantially exceed observations, while, similar to the case for Hurricane Ike, performance for Tp generally seems good in spite of numerous potential sources of uncertainty. Anomalous timing and magnitude of some simulations can be related directly to storm tracks. For example, although the timing is well synchronized in the three cases for Katrina, discrepancy in wave heights at buoy 42001 (Figure 6a) appears to be explained by the proximity of the respective tracks to the buoy when intensity was highest. Given that the historic track (solid blue line, Figure 3) so closely matches the observed track, but simulated Hs exceeds observations by approximately 35%, it appears that high wind speeds are substantially biasing the extremes. This also seems likely at buoy 42060 during Hurricane Maria (panel f), where although simulated storm tracks appear realistic, Hs dramatically exceeds observations.
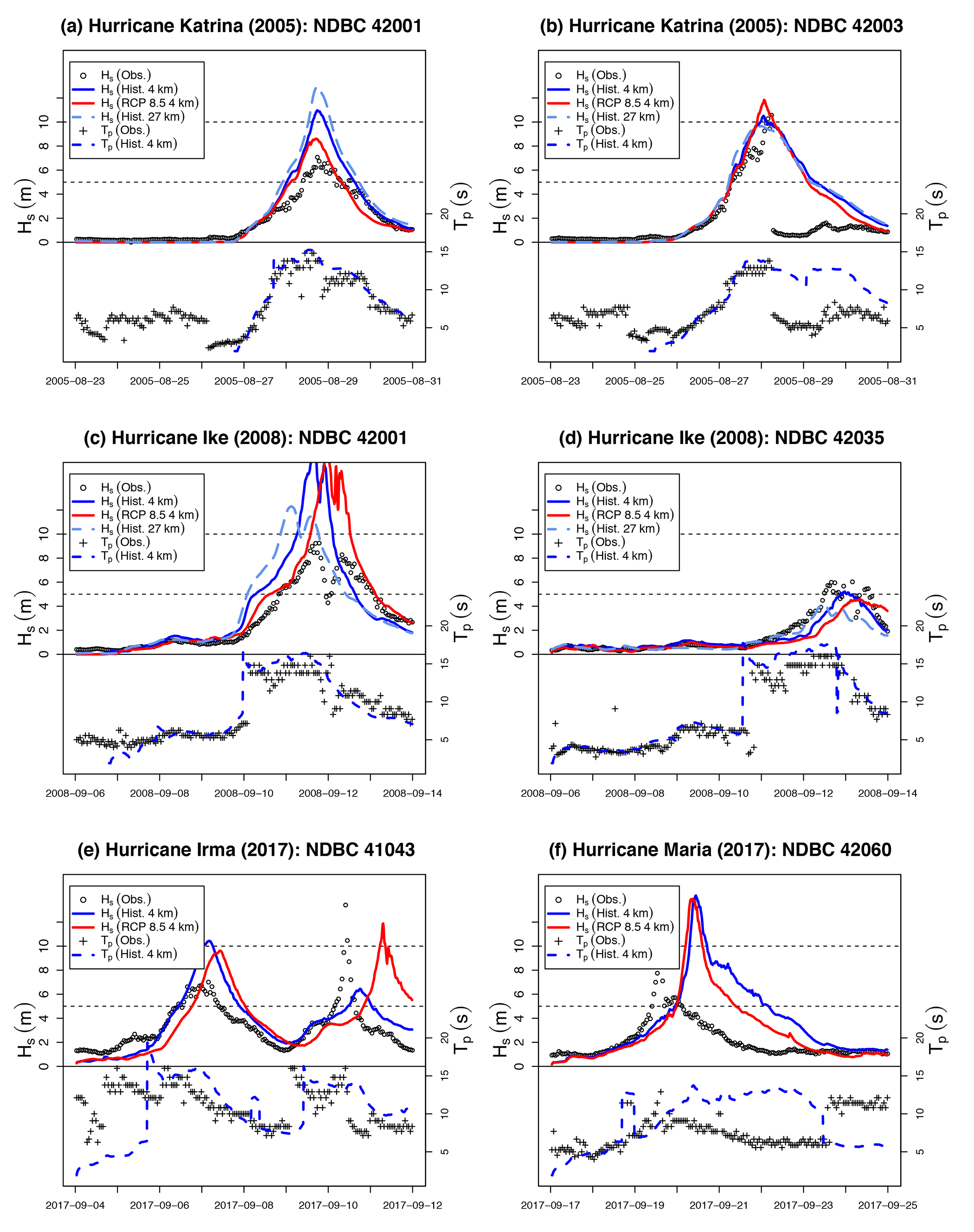
Figure 6. Wave parameters at selected buoys where conditions were the most energetic due to Hurricanes Katrina, Ike, Irma, and Maria simulated with historical 4 km winds (blue), historical 27 km winds (light blue, where applicable), and RCP8.5 winds (red), compared with observations (circles and crosses) at buoys that observed the largest waves in each case. > High res figure
|
Notably, Y. Chen and Yu (2017) also raise the issue of high simulated Hs at buoy 42001 (see their Figure 6), during Katrina. They speculate that the hurricane’s rotation created offshore winds on its left side, thus resulting in fetch-limited conditions due to the coastline, which might be more poorly represented by the modeling setup. We assert that there may be more to this issue because our results appear to show consistent overestimation of peak Hs in a number of cases where fetch is essentially unlimited. Indeed, Y. Chen et al. (2018) call for more expansive studies by looking at additional hurricanes in order to draw more robust conclusions.
Conclusions
We presented two 50-year simulated global wave climate data sets under +1.5°C and +2.0°C warming scenarios. Changes in extreme wave height may be evident, particularly increases in the tropical North Pacific and Atlantic basins, and possible reduction in the tropical South Pacific. However, these changes are characterized by poor sampling of TCs, which introduces uncertainty, and in turn motivates the need for much longer duration data sets. Furthermore, recent research suggests that the use of fixed SST boundary conditions in CESM may introduce regional bias in storm track density, so we advise caution in interpretation. Simulations of individual hurricanes using the WRF model with observed SSTs suggest that extreme wind speeds, and resulting wave heights, are likely to be excessive. Noting also that evolution of simulated storm track, intensity, and translation speed contribute substantially to variability in output wind and wave characteristics, we echo Y. Chen et al. (2018) and advocate for broader ensemble studies of this type. Such data sets would add value to COWCLIP and help advance the investigation of the effects of atmosphere-ocean processes on extreme wave climate.